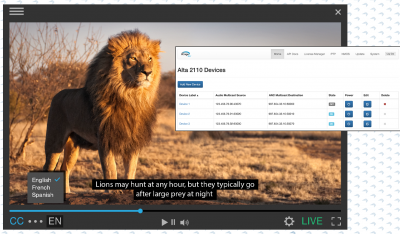
Through a strategic integration with Amazon Web Services (AWS), EEG Video is pushing new boundaries in closed captioning, helping customers harness the flexibility and efficiency of the cloud with innovative solutions that support closed captioning, accessibility and metadata processing in broadcast, post production, streaming, live event production, government, and education. Using AWS Cloud Digital Interface (CDI) network technology, EEG has expanded its Alta IP caption and subtitle encoder capabilities to include support for real-time captioning for uncompressed live video over IP.
For modern audiences, it’s hard to remember a time when closed captioning wasn’t a standard menu option. Across the US and much of the world, accessibility to the essential service became a government mandate via legislation set in the 1990s. Since then, encoding and decoding technology for closed captioning has advanced, but its evolution has been fast tracked by the cloud. Through strategic integration with Amazon Web Services (AWS), technology company EEG Video is pushing new boundaries in the space, helping customers harness the flexibility and efficiency of the cloud with innovative workflow solutions that support closed captioning, accessibility and metadata processing in broadcast, post production, streaming, live event production, government, and education. Using AWS Cloud Digital Interface (CDI)network technology, EEG has expanded its Alta IP caption and subtitle encoder capabilities to include support for real-time captioning for uncompressed live video over IP.
“One of the promises of the SMPTE 2110 standard is that you can deliver video, audio, and ancillary data separately, and that’s important for a device like a closed captioning encoder that doesn’t need to be connected to an ultra high resolution video source to operate, which could save bandwidth,” said Bill McLaughlin, CTO, EEG Video. “However, technology is changing so quickly and SMPTE 2110 is not a public cloud technology. Using AWS CDI with Alta, we can offer the best of both worlds – the benefits of SMPTE 2110 and the scalable resources of AWS.”
The largest closed captioning and subtitle delivery network in the world, EEG’s iCap provides round-the-clock access to real-time captioners and is hosted on AWS. Connecting IP workflows to the iCap Network, Alta harnesses AWS CDI to ensure reliable, low latency transport of uncompressed live video. Captioning through Alta can be done via an iCap human typist or through artificial intelligence (AI), and broadcasters often use a combination of the two approaches based on budget and project requirements. Beyond broadcast or OTT programming, captioning is now also prevalent at events and in large-scale venues, and with the rise of video conferencing, is increasingly being offered in those platforms, leading to more accessible communication. Powerful cloud-based solutions, like AWS CDI, allow service providers, including EEG Video, to help customers adapt workflows with the new lightning pace of innovation.
“Fifteen years ago, it made sense to invest in a data center, because it was easier to predict what customers were going to want and need long term. Today, the live media industry is changing far too quickly to be able to make sizable investments like that with confidence, so many companies are now software-driven, which is made possible by the cloud,” NAME explained. “Using AWS, independent software vendors like us can more easily take our specialties, such as captioning, to the public cloud, and with functionality provided by technology like AWS CDI, integrate without concerns about network drivers or hardware-related issues, and that’s very helpful for building applications.”
A typical customer setup with Alta will include a central hub from a common vendor, such as Evertz, running on an AWS CloudFormation template or wherever their overall broadcast infrastructure systems are hosted for routing videos, and this is also where clipping, resolution transformation and similar tasks would be completed. When a feed needs captioning, it would then be sent to an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance that is hosting EEG channels, then ingested and captioning would be added, either via human or automated methods. From there, the captioned feed would be re-ingested into the central hub for recording or other applications. The feed could also be sent directly to AWS Elemental MediaLive for encoding and repurposing feed data. AWS Elemental MediaPackage can then be used to make an HLS stack that can help generate a link for use on different player sites. Where a video is being hosted, the HLS URL can be used to output closed captions on a web player.
In integrating AWS CDI with Alta, the goal for EEG Video was not to fundamentally change its operational workflow around closed captioning, but rather save customers money while broadening capabilities. EEG Video’s use of the cloud is also helping it globalize what has traditionally been a regionalized market.
McLaughlin concluded, “AWS is allowing to do what we’ve always done but in the cloud. This allows us to offer a spin up/spin down opex model with the polish deserving of a major broadcast as many of our customers navigate business challenges driving them toward maximizing flexibility in their workflows.”